Section One:
Addressing the NEED
Africa has a NEED to provide nutrition for its people who are:
- Malnourished children under the age of 5 years who have stunted growth as a result; and
- Pregnant and breast-feeding mothers who are nutrient deficient.
Commonly stated key statistics of malnutrition prevalence in Zambia (Unicef, 2007):
- Incidence of wasting (low weight for height) = 5%
- Incidence of underweight (low weight for age) = 15%
- Incidence of stunting (low height for age) = 45%
Historical prevalence of vitamin A and Iodine deficiencies in both groups (children and women).
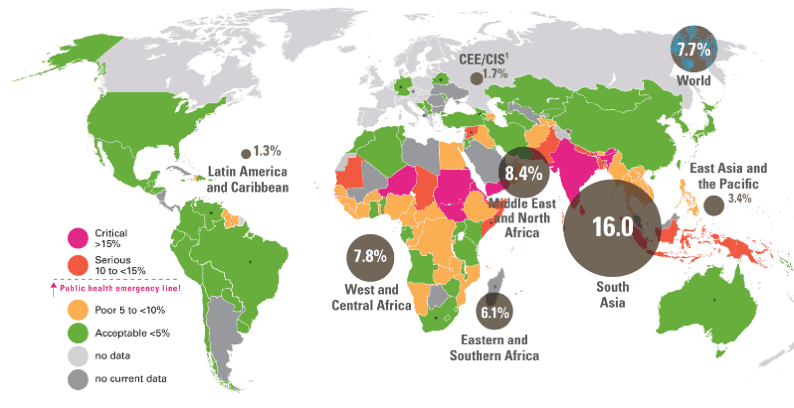
Percentages of children under 5 years who are wasted – 2016
Background: micronutrient focus
- Shortages of vitamins and minerals often are referred to as micronutrient deficiencies. Not only do protein–energy malnutrition and micronutrient deficiencies overlap, but a lack of one micronutrient is typically associated with deficiencies of other micronutrients.
- Micronutrients enable the body to produce enzymes, hormones and other substances that are essential for proper growth and development.
- Consuming foods with a high content of absorbable micronutrients is considered the best means for preventing micronutrient deficiencies.In communities where supplies of nutrient dense foods are unavailable, specific preventive and curative interventions are required.
- There is growing consensus on the importance of multiple micronutrient interventions in populations with a high prevalence of malnutrition. However, synergistic and antagonistic interactions between micronutrients must be taken into consideration during the development of appropriate formulations.
- Diet-based strategies are the most appropriate approach for a sustainable control of micronutrient deficiencies. Priority should be given to vulnerable populations such as pregnant women and children. Supplementation should be mandated in cases of a specific deficiency when other approaches are too slow.
- Vitamin A, Iodine, Iron and Zinc are the most important in global public health terms; their deficiency represents a major threat to the health and development of populations worldwide, but particularly children and pregnant women in low-income countries.
Affects of malnutrition in women and children:
- Severe malnutrition contributes to nearly 50% all deaths in children less than 5 years of age.
- Malnutrition causes diminished physical development and a compromised immunity that causes higher incidence of infectious diseases.
- Stunting caused by under nutrition in children:
- Predicts poorer cognitive test scores and higher absenteeism.
- Has a significant educational and economic consequence at the individual, household and community level.
- Maternal malnutrition increases the risk of poor pregnancy outcomes including obstructed labour, premature or low-birth-weight babies, retardation and postpartum hemorrhage.
- Severe anaemia during pregnancy is linked to increased mortality at labour.
- Child malnutrition impacts on economic productivity.
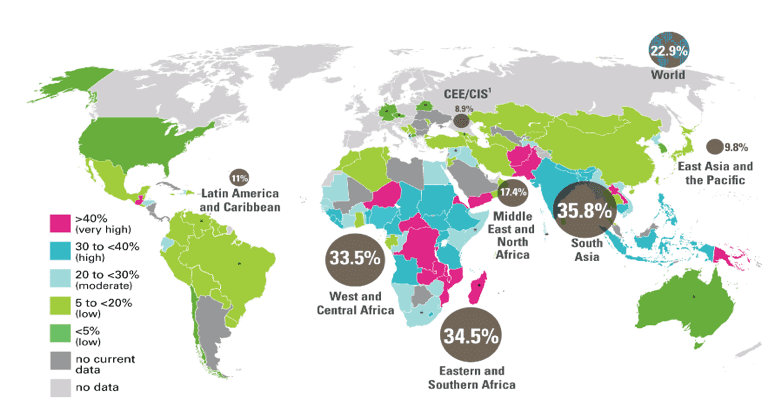
Map indicating rates of under-nutrition in the world
Pregnant and Breastfeeding Mothers
- Helping women of reproductive age to achieve optimal nutritional status at conception is an excellent preventive measure.
- A focus on the pre-conception period has been recently introduced as a complement to the key phase of the 1000 days of pregnancy and first two years of life.
- A well-nourished mother is the first step of stunting prevention, decreasing chances of the baby being born of low birth-weight, which is the first risk factor for future malnutrition.
- A woman’s requirement for numerous micronutrients increases during pregnancy to provide for the growing fetus.
- It is important that pregnant women are aware that many micronutrients are interrelated in function, so a deficiency in one micronutrient might affect the utilisation of other micronutrients.

Important points to consider:
- Some 42% of sub Saharan African population is under 15 years of age – the future of the productive populace.
- Children must be reached with correct within first 2 years.
- Chronic malnutrition is largely irreversible.
WHY do we need to respond to this NEED?
The ‘Cost of Hunger in Africa’ (COHA) study highlights the economic and social implications:
- COHA estimate that the economic impact of malnutrition falls somewhere between 9 and 16.5% of GDP.
- The study estimated that the undernourishment of children generates health costs of between 1 – 11% of total government health budget
- The study estimates that a large proportion of sufferers of malnutrition and stunted growth (69 – 81%) do not seek medical attention.
- It is estimated that 7 – 16% of all grade repetitions in schools are associated with malnourished children. Some 90% of grade repetition occurs in primary schools.
- Some 8 – 44% of child mortality is associated with undernutrition.
- The study estimates that a reduction of malnutrition by half by 2025 would generate annual savings of up to $376 million in affected countries.
Section Two:
The Solution
Yabhusta Power Supply
Formed in 2007, the Power Supply formulation was created from extensive, long-term research conducted in collaboration with local and international nutritionists. Power Supply is fortified with specifically formulated nutrients required to support enhanced physical and mental performance.
Over a million meals of Power Supply are consumed annually with excellent results.

Supplement Solution:
Two instant porridge products and one Mageu drink have been custom designed to directly address the needs of the Zambian Health Ministry.
- Yabhusta Power Supply – Children under 5 years of age
- Yabhusta Power Supply – Pregnant & breastfeeding women
- Yabhusta Power Supply Instant Mageu
Experienced Nutritionist
The product formulations were created by well known and highly regarded nutritionist, Mrs. Willa Haasbroek.
A summary of Mrs. Haasbroek experience:
- Bachelor of Science degree – 1983
- Bachelor of Science Honours in Microbiology – 1984
- Masters of Science in Microbiology – 1986
- Developed B-Immune range of probiotic supplements for government hospital and clinic programs.
- Responsible for product development and Quality Assurance department and successfully launched household South African brands e.g. ProNutro Toddlers, Isotonic Game, Trotters Jelly and many more.
-
Yabhusta Power Supply – Children under 5 years
Formulation base: Non-GMO maize, soya isolate and sorghum
Preparation: Instant – just add clean water or milk
Meal size: 50g dry powder
Frequency: Twice per day
Nutritional Information:
| Nutrient | Units | Per 100g | Per Portion (50g) | NRV Individuals 4 years and older |
| Energy | Kj | 1590 | 795 | |
| Protein | g | 12,79 | 6 | 23% |
| Carbohydrate | g | 69,7 | 35 | |
| Fat | g | 6,97 | 3 | |
| Fibre | g | 6,95 | 3 | |
| Vitamins | ||||
| Vitamin A | mcg RE | 510 | 255,0 | 57% |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) | mg | 0,7 | 0,4 | 58% |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | mg | 0,50 | 0,3 | 38% |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | mg | 9,00 | 4,5 | 56% |
| Vitamin B5 (Calcium d- panthothenate) | mg | 2,50 | 1,3 | 50% |
| Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) | mg | 0,7 | 0,4 | 41% |
| Vitamin B12 (Cyanocobalamin) | ug | 1,3 | 0,7 | 54% |
| Vitamin C | mg | 40 | 20,0 | 40% |
| Vitamin D3 | mcg | 5 | 2,5 | 33% |
| Vitamin E | mg | 5 | 2,5 | 33% |
| Folic Acid | mcg | 200 | 100,0 | 50% |
| Minerals | ||||
| Calcium | mg | 800 | 400 | 62% |
| Iron | mg | 18 | 9 | 100% |
| Zinc | mg | 3 | 2 | 27% |
| Elemental Iodine | mcg | 50 | 25 | 33% |
| Sodium | mg | 451,8 | 226 |
Impacts of formulation:
- This formulation is high in 11 essential vitamins, including calcium, iron and iodine. It is also a source of zinc.
- Vitamin A is particularly important for ensuring optimal eye development in the embryo. It helps form and maintains healthy teeth, bones, soft tissue, mucus membranes, and skin.
- Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) helps the body cells convert carbohydratesinto energy. Getting enough carbohydrates is vital for a child. It is also essential for heart function and healthy nerve cells.
- Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) works with the other B vitamins. It promotes for body growth and the production of red blood cells.
- Vitamin B6 (Pyrodoxine) helps form red blood cells and maintains brain function. This vitamin also plays an important role in the proteins that are part of many chemical reactions in the body. The more proteinyou eat the more pyridoxine your body requires.
- Vitamin B9 (Folate)works with vitamin B12 to help form red blood cells. It is needed for the production of DNA, which controls tissue growth and cell function. Without adequate levels of folate, cells cannot divide and replicate and therefore growth is restricted.
- Vitamin B12 is important for metabolism and the functioning of the central nervous system.
- Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) is an antioxidant that promotes healthy teeth and gums. It helps the body absorb iron and maintain healthy tissue. It also promotes wound healing.
- Vitamin D is also known as the “sunshine vitamin,” since the body makes it after being in the sun. Vitamin D enables calcium absorption. Calcium is required for the normal development and maintenance of healthy teeth and bones. It also helps maintain proper blood levels of calcium and phosphorus.
- Vitamin E is an antioxidant also known as tocopherol. It helps the body form red blood cells and use of vitamin K.
- Iron is a component of a number of essential proteins, including hemoglobin, which is essential for transporting oxygen in the blood. The absorption of iron from plant sources is increased when more vitamin Cis available.
- Iodine plays an important role in development of the central nervous system. In extreme cases, iodine deficiency can lead to cretinism; a disorder that involves severely stunted physical and mental growth.
-
Yabhusta Power Supply – Pregnant & breastfeeding women
Formulation base: Non-GMO maize, soya isolate and sorghum
Preparation: Instant – just add clean water or milk
Meal size: 80g dry powder
Frequency: Once per day
Nutritional Information:
| Nutrient | Units | per 100g | Per Portion (80g) | NRV Individuals 4 years and older |
| Energy | Kj | 1590 | 1272 | |
| Protein | g | 12,79 | 10 | 23% |
| Carbohydrate | g | 69,7 | 56 | |
| Fat | g | 6,97 | 6 | |
| Fibre | g | 6,95 | 6 | |
| Vitamins | Units | per 100g | Per 80g portion | NRV Individuals 4 years and older |
| Vitamin A | mcg RE | 1625 | 1300 | 181% |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) | mg | 1,75 | 1,4 | 146% |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | mg | 2,00 | 1,6 | 154% |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | mg | 22,50 | 18,0 | 141% |
| Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) | mg | 0,00 | 0,0 | 0% |
| Vitamin B12 (Cyanocobalamin) | ug | 3,50 | 2,8 | 146% |
| Vitamin C | mg | 150,00 | 120,0 | 150% |
| Vitamin D3 | mcg | 6,25 | 5,0 | 42% |
| Folic Acid | mcg | 750,00 | 600,0 | 188% |
| Vitamin K | mcg | 112,50 | 90,0 | 94% |
| Minerals | ||||
| Calcium | mg | 1250 | 1000,0 | 96% |
| Elemental Iron | mg | 33,75 | 27,0 | 188% |
| Elemental Zinc | mg | 15 | 12,0 | 136% |
| Elemental Iodine | mcg | 275 | 220,0 | 183% |
| Elemental Magnesium | mg | 437,5 | 350,0 | 104% |
| Elemental Selenium | mcg | 81,25 | 65,0 | 148% |
| Sodium | mg | 451,8 | 361,4 |
Impacts of formulation
- Vitamin A is particularly important for ensuring optimal eye development in the embryo. It helps form and maintain healthy teeth, bones, soft tissue, mucus membranes, and skin.
- Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) assists in the conversion of carbohydratesinto energy. Getting enough carbohydrates is very important during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It is also essential for heart function and healthy nerve cells.
- Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) interacts with the other B vitamins for body growth and the production of red blood cells.
- Vitamin B3 (Niacin) helps maintain healthy skin and nerves. It also has cholesterol-lowering effects at higher doses.
- Vitamin B9 (Folate)works with vitamin B12 to help form red blood cells. Folate is vital for pregnant women. It is needed for the production of DNA, which controls tissue growth and cell function. Without adequate levels of folate, cells cannot divide and replicate and therefore growth is restricted. Low levels of folate are linked to birth defects such as spina bifida.
- Vitamin B12 is important for metabolism and supports the central nervous system. Vitamin B12 is involved in converting folateto the form in which it can be absorbed by the body, known as methyl-tetrahydrofolate.
- Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid) is an antioxidant that promotes healthy teeth and gums. It helps the body absorb iron and maintain healthy tissue. It also promotes wound healing.
- Vitamin D is also known as the “sunshine vitamin,” since the body makes it after being in the sun. Calcium is required for the normal development and maintenance of healthy teeth and bones. It also helps maintain appropriate levels of calcium and phosphorus in the blood.
- Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant known as tocopherol. It supports the production of red blood cells and use of vitamin K.
- Vitamin K is not listed among the essential vitamins, but without it blood would coagulate (clot). Studies suggest that it is important for bone health and influence the absorption of Calcium.
- Pantothenic acid is essential for the metabolism of food. It also plays a role in the production of hormones and cholesterol.
- Iron is a component of a number of essential proteins, including hemoglobin which is essential for transporting oxygen in the blood. The absorption of iron from plant sources is increased when vitamin Cis available.
- Zinc deficiency during pregnancy is associated with an increased risk of pregnancy complications, including high blood pressure and urinary protein concentrations and premature rupture of membranes (when a woman’s pregnancy water breaks).
- Copper improves brain function, soothes arthritis, helps in skin care, eliminates throat infections, corrects hemoglobin deficiency, prevents heart diseases, and boosts immunity. It is commonly associated with the uptake of iron and the facilitation of a properly functioning circulatory system.
- Iodine deficiency during pregnancyis serious for both the mother and the baby. It can lead to high blood pressure during pregnancy for the mother, and mental retardation for the baby. Iodine plays an important role in development of the central nervous system.
- Magnesium is required for the proper growth and maintenance of bones. Magnesium is also required for nerve and muscle functioning. During pregnancy it is used to treat high blood pressure and other pregnancy complications.
-
Yabhusta Power Supply – Instant Mageu
Formulation base: Non-GMO maize
Preparation: Instant – just add clean water
Meal size: 120g dry powder males 1 litre
Frequency: Once per day

Nutritional Information:
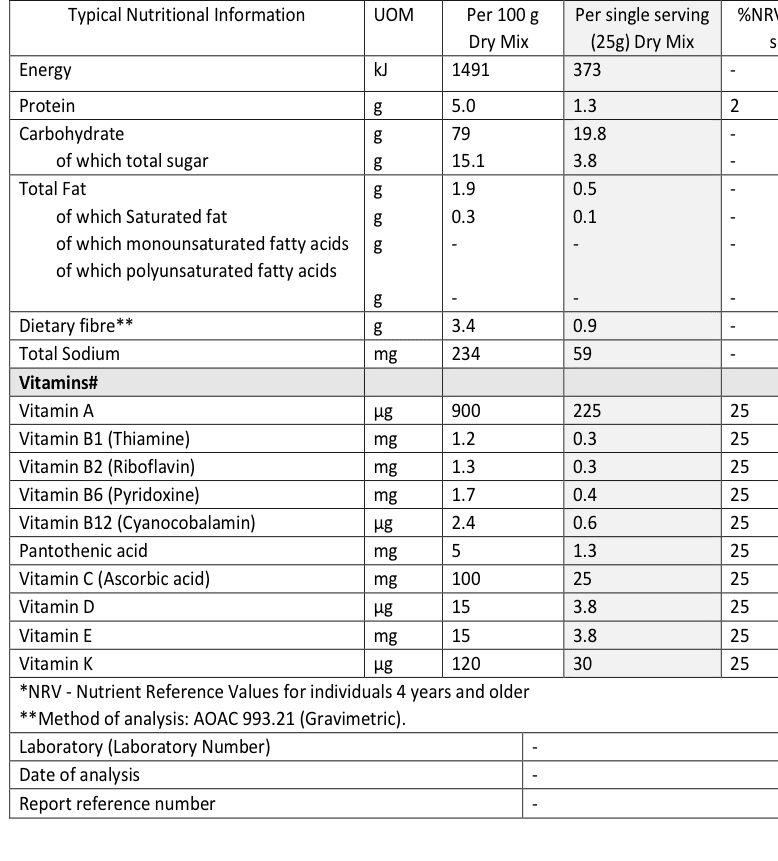
Impacts of formulation:
- Power Supply instant Mageu was developed with due respect for the long tradition of this important African drink. Also known as maHewu, amaRhewu or amaHewu, it is a traditional non-alcoholic maize drink.
- The excellent taste and texture is the same as the traditional home brewed Mageu, and makes a refreshing drink for anyone of any age.
- Power Supply instant Mageu is loaded with vitamins for an added energy boost.
- High in energy
- High in carbohydrates
- Source of protein
- Source of vitamin
Manufacture Facility

Our products are produced by Westpack Contract Packers, a leading South African contract food manufacturer and packaging services provider.
Westpack focuses on quality, health and safety.
Accreditation:
- HACCP studies in place with continuous improvement
- Quality Management System ISO 22000 FSSC accredited
- BBBEE rated level 3
- Halaal accredited (SANHA)
- Kosher accredited
- PRP’s in place
- Environmental Risk Assessment completed
- Allergen studies completed and identified
- Pathogen monitoring
Facility details:
- Westpack is situated in Pinetown 35km northwest of Durban.
- The facility of 9 673m2 is racked for 3 608 pallet positions.
- The production area is 2 803m2, including the mezzanine area.
- The facility has 26 packing lines and 3 state of the art blending facilities
- Westpack has in-house engineering capabilities able to offer upgrades to machines for new product innovations and for high speed packing machine rebuilds and reconditioning.
Westpack’s Clients:










Leave A Comment